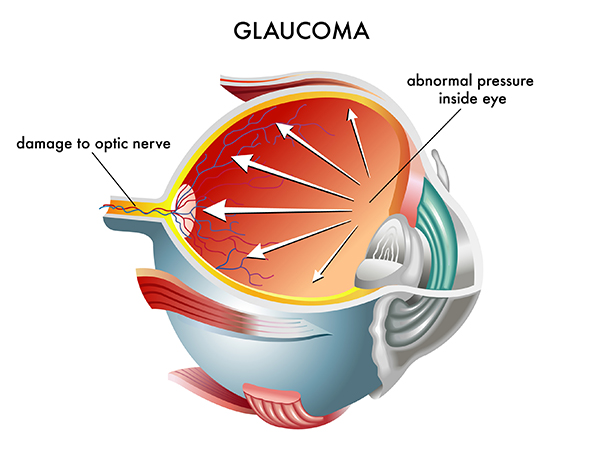
What is Glaucoma?
- Glaucoma is an eye disease that gradually steals vision. There are typically no early warning signs or painful symptoms of open-angle glaucoma. It develops slowly and sometimes without noticeable sight loss for many years.
- Most people who have open-angle glaucoma feel fine and do not notice a change in their vision at first because the initial loss of vision is of side or peripheral vision, and the visual acuity or sharpness of vision is maintained until late in the disease.
- By the time a patient is aware of vision loss, the disease is usually quite advanced. Without proper treatment, glaucoma can lead to blindness. The good news is that with regular eye exams, early detection, and treatment, you can preserve your vision.
Eye Exams
Because open-angle glaucoma has few warning signs or symptoms before damage has occurred, it is important to see a doctor for regular eye examinations. If glaucoma is detected during an eye exam, your eye doctor can prescribe a preventative treatment to help protect your vision.
Optic Nerve Damage
In open-angle glaucoma, the angle in your eye where the iris meets the cornea is as wide and open as it should be, but the eye’s drainage canals become clogged over time, causing an increase in internal eye pressure and subsequent damage to the optic nerve. It is the most common type of glaucoma, affecting about four million Americans, many of whom do not know they have the disease.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF GLAUCOMA?
There are many different types of glaucoma, but the most common type in the United States is called open-angle glaucoma — that’s what most people mean when they talk about glaucoma. Other types of glaucoma are less common, like angle-closure glaucoma and congenital glaucoma.
Angle-closure glaucoma can cause these sudden symptoms:
- Intense eye pain
- Upset stomach (nausea)
- Red eye
- Blurry vision
If you have these symptoms, go to your doctor or an emergency room now
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF GLAUCOMA?
- At first, glaucoma doesn’t usually have any symptoms. That’s why half of people with glaucoma don’t even know they have it.
- Over time, you may slowly lose vision, usually starting with your side (peripheral) vision — especially the part of your vision that’s closest to your nose. Because it happens so slowly, many people can’t tell that their vision is changing, especially at first.
- But as the disease gets worse, you may start to notice that you can’t see things off to the side anymore. Without treatment, glaucoma can eventually cause blindness.
AM I AT RISK OF GLAUCOMA?
Anyone can get glaucoma, but some people are at higher risk. You’re at higher risk if you:
- Are over age 40
- Are African American or Hispanic/Latino and over age 40
- Have a family history of glaucoma
- Are Diabetic
- Are Using steriod medication or drops
- Have enlarge optic nerve or large cup-disc ration ( Large C/D)
- Have higher intra-ocular pressure (IOP)
- Are very nearsighted
- Have high blood pressure
It is important to have your eyes examined regularly. Your eyes should be tested:
- before age 40, every two to four years
- from age 40 to age 54, every one to two years
- from age 55 to 64, every year
- after age 65, every six to 12 months
REASONS WHY YOU MIGHT NEED A COMPREHENSIVE GLAUCOMA EXAM
- Glaucoma Suspect due to Large cupping ( Large C/D)
- Glaucoma Suspect due to different C/D ratio
- Glaucoma Suspect due to higher IOP’s
- See Risks factor above
Related Information
Opening Hours
| Monday – Thursday | 8:30 – 5:00 |
| Friday | 8:30 - 4:00 |
| Saturday-Sunday | Closed |
| Open During Lunch |